How Does a Hash Help Secure Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we think about security and data integrity. Central to this innovation is the humble hash. But what exactly is a hash, and how does it contribute to the security of blockchain technology? Let’s dive into hashing and its important role in the blockchain world.
What is a Hash?
Definition of a Hash
A hash is like a fingerprint of data. It is a unique string of characters generated from the input data, regardless of the size of that data. Think of it as taking a snapshot of information and reducing it to a fixed size. This process ensures that even the smallest change to the input will produce a completely different hash, which is extremely useful for verifying data integrity.
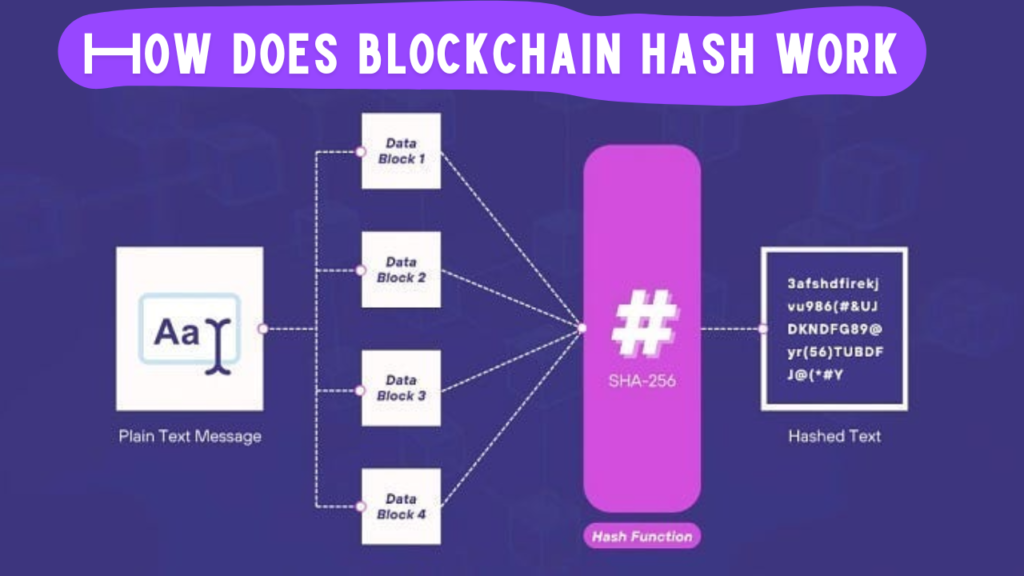
How Hashing Works
Hashing uses a mathematical algorithm to convert input data into a hash. This transformation is one-way, meaning you cannot reverse-engineer the original data from the hash. This feature is fundamental to its security features. Imagine trying to figure out what a cake looks like from its slice impossible, right? This is how hashing works.
The Role of Hashing in Blockchain
Ensuring Data Integrity
In blockchain, each piece of data or transaction is hashed and added to a block. This ensures that any alteration to the data will change the hash, allowing tampering to be detected. It’s like putting a tamper evident stamp on your favorite jar of cookies.
Enhancing Security
The security provided by hashing in blockchain is multifaceted. First, it ensures that records are immutable. Once a block is added to the blockchain, the hash makes it nearly impossible to change any data within that block without identifying it. Imagine trying to replace a single book in a large library with a forgery. If the books are hashed, any changes will be immediately apparent.
Immutable Records
Each block in a blockchain has its own hash and the hash of the previous block, creating a chain of blocks. This link creates an immutable ledger of transactions. It is like a chain where each link depends on the previous one. Break one link, and the entire chain is compromised.
Hashing and Cryptography
Cryptographic Hash Functions
Cryptographic hash functions are the backbone of blockchain security. They are designed to be collision resistant (no two different inputs produce the same hash) and quick to compute. Functions such as SHA-256 are commonly used, which ensure strong security.
Popular Hash Algorithms
The most popular hash algorithms in the blockchain space include SHA-256, used by Bitcoin, and Keccak-256, used by Ethereum. These algorithms are selected for their ability to provide high levels of security and performance.
Block Creation and Validation
Proof of Work
Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism that requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles using hashing. This process validates transactions and creates new blocks, ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain.
Mining and Hashing
Miners compete to solve a hash puzzle, and the first person to solve it has to add the next block to the blockchain. This process is computationally intensive and ensures that adding a new block is a costly effort, preventing fraudulent activities.
Hash Pointers in Blockchains
Linking Blocks Together
Hash pointers link each block to its predecessor. This creates a chain of blocks that is tamper-proof because changing a single block would require recomputing the hashes of all subsequent blocks, a near-impossible task due to the computational power required.
Preventing Tampering
If someone tries to tamper with the block, the hash changes, breaking the chain. It is this instant detection mechanism that makes blockchains so secure. It is like trying to turn a bead into a string of pearls; You will have to replace the entire wire.
Merkle Trees
Structure of Merkle Trees
A Merkle tree is a type of data structure that allows for efficient and secure verification of large data sets. They break the data into smaller pieces, hash them, and then hash those hashes in pairs until a single hash, called the root hash, is produced.
Benefits of Merkle Trees
Merkle trees enable quick and easy verification of data integrity, without having to verify each piece of data. This structure is highly efficient and adds an extra layer of security to the blockchain.
Hashing in Different Blockchain Applications
Bitcoin
Bitcoin relies heavily on SHA-256 hashing to secure its transactions and validate new blocks. The security of the entire network depends on this strong hashing algorithm.
Ethereum
Ethereum uses Keccak-256, a variant of SHA-3, for its hashing needs. It ensures data integrity and security within the Ethereum network, supporting its complex smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Other Applications
In addition to Bitcoin and Ethereum, many other blockchain applications use hashing for security, including supply chain management, digital identity verification, and secure voting systems. Each of these applications takes advantage of the immutability and integrity provided by hash functions.
Potential Weaknesses of Hashing
Hash Collisions
Rarely, hash collisions (where two different inputs produce the same hash) may occur. Cryptographic hash functions are designed to mitigate this risk, but it is still a theoretical weakness.
Quantum Computing Threats
Quantum computing is a future threat to current hashing algorithms because of its ability to break these secret methods. The blockchain community is actively researching quantum-resistant algorithms to stay ahead of this threat.
Future of Hashing in Blockchain
Innovations and Developments
The future of hashing in blockchain is bright, with ongoing innovations aimed at improving security and efficiency. New hashing algorithms and enhancements to existing ones are constantly being developed.
Evolving Security Measures
As threats evolve, so do safeguards. The blockchain community is actively working to address potential threats and ensure that hashing remains a strong defense mechanism.
Conclusion
Hashing is the so-called hero of blockchain technology. It ensures data integrity, security, and changeability of records, which form the backbone of blockchain’s revolutionary capabilities. As technology advances, hashing will only increase in importance, securing the future of digital transactions.
FAQs
Q1: What is a hash in simple terms?
A hash is a unique string of characters generated by a mathematical algorithm from the input data, which works like a digital fingerprint.
Q2: How does hashing ensure data integrity in a blockchain?
Hashing ensures that any change to the data changes the hash, making tampering easier to detect.
Q3: What is the role of hashing in mining?
Hashing is used in mining to solve complex puzzles that validate and add new blocks to the blockchain, securing the network.
Q4: Are there any risks associated with hashing?
While generally safe, potential risks include hash collisions and future risks from quantum computing.